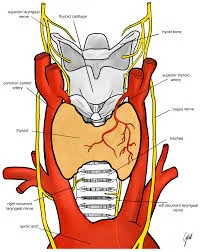
Objective: This study was designed to describe the various anatomical relations of the recurrent laryngeal
nerve (RLN) during thyroid surgery in a Central African population.
Patients and methods: A prospective study was conducted between January 2012 and December 2012
in 5 otorhinolaryngology and head and neck surgery departments in Cameroon and Gabon. All patients
undergoing total or subtotal thyroidectomy or loboisthmectomy with recurrent laryngeal nerve dissec-
tion, with no history of previous thyroid surgery, RLN dissection or tumour infiltration of the RLN, were
included.
Results: Fifty-six patients were included, corresponding to 36 loboisthmectomies and 20 total or subtotal
thyroidectomies. A total of 62 recurrent laryngeal nerves were identified: 32 on the right and 30 on the
left. The course of the recurrent laryngeal nerve in relation to branches of the inferior thyroid artery (ITA)
was retrovascular in 53.1% of cases on the right and 76.6% of cases on the left; transvascular in 15.6% of
cases on the right and 13.4% of cases on the left. The course of the recurrent laryngeal nerve was modified
by thyroid disease in 12.9% of cases. Six cases (9.7%) of extralaryngeal division of the recurrent laryngeal
nerve were observed. No case of non-recurrent nerve was observed in this series.
Conclusion: The anatomical relations of the recurrent laryngeal nerve with the inferior thyroid artery
were very inconstant in this series and were predominantly retrovascular or transvascular in relation
to the branches of the artery. The presence of extralaryngeal branches and modification of the course
of the nerve by thyroid disease also introduced additional difficulties during recurrent laryngeal nerve
dissection. The anatomical relations of the right recurrent laryngeal nerve in this African population differ
from the classically described prevascular course.